Research
Much of my work exists at the border of where our instruments can resolve features within galaxies.
This allows for important validation of high redshift techniques on nearby and nearby low mass galaxies,
but also enables the development of
new methods that allow us to push deeper into the semi-resolved universe.
Bonus is that we can learn new things about our near-ish neighbors.
What I'm most interested in is how individual galaxies grow their stellar mass over time,
and how much impact their external and internal environment impacts this. The low redshift universe grants us access to some of the smallest, faintest,
and most plentiful galaxies. These small galaxies are the most sensitive to environment and therefore promise to tell us the most about how environment drives galaxy evolution.
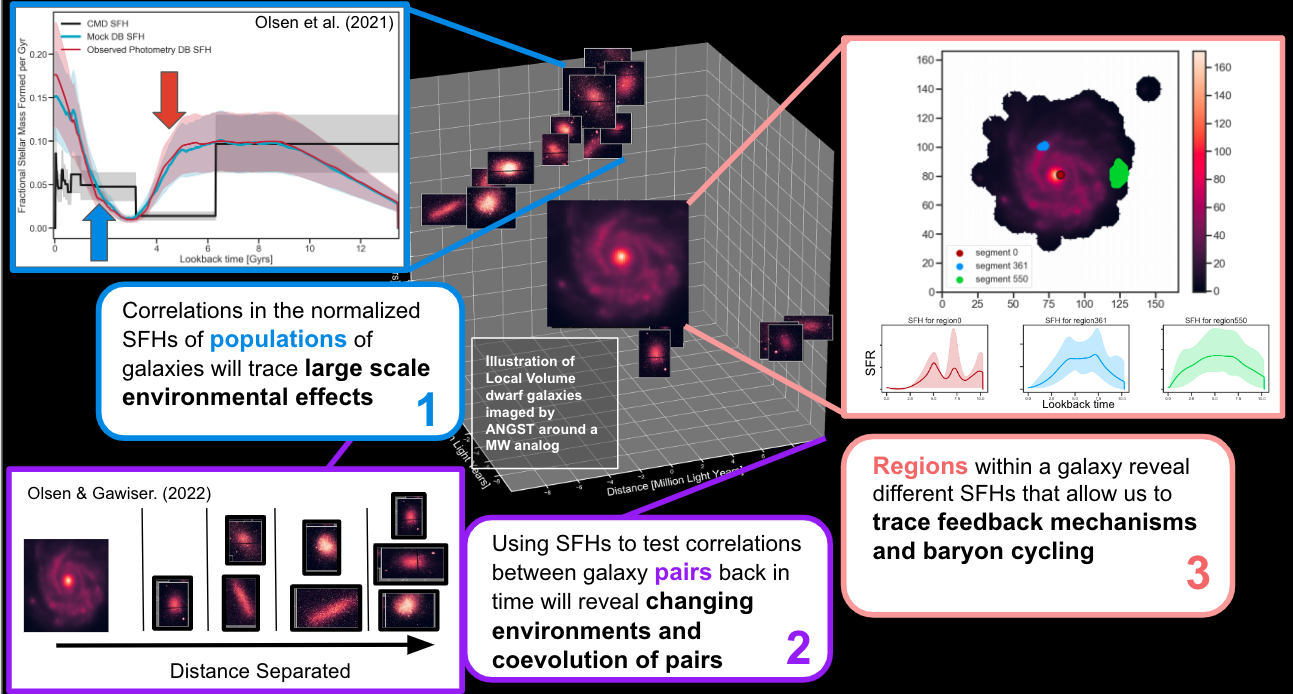
SEDs and CMDs Find Synchronized Star Formation in Local Volume Dwarf Galaxies
There are two main ways of reconstructing
a galaxy's star formation history (SFH). If it is nearby, you can look at the color and brightness of its stars and infer the ages of
its stellar populations. If it is far away you can sum up
the total flux through bands at different wavelengths and then fit the galaxy's spectrum and infer the populations that
contribute to it's total light. The first is the color-magnitude diagram method of SFR reconstruction and the second is the spectral energy distribution (SED) fitting method.
I do the second one, but seeing how the two compare is an important validation!
We took galaxies that were close enough to resolve individual stars, yet far away enough to have reliable integrated photometry
and compared their SFHs. Not only did these compare well, but we found that the SFHs of the galaxies in our sample
decreased and increased their star formation
synchronistically at specific epochs in spite of being separated by great distances!!
Looking for confformity in Local Volume galaxies
Galactic conformity refers to shared property between pairs of galaxies. For example, the average color or SFR of galaxies near
a central galaxy may be similar to the properties of that central galaxy. These types or tests are usually performed on large populations
to find in-situ trends in galaxy evolution. We investigated whether the galaxies having synchronized star formation might also show conformity.
Using the SFHs of the galaxies allowed us to read the properties off the SFHs at different epochs. We did find conformity, but not in
the galaxies showing synchronized star formation, which suggests that synchronized star formation and conformity are sensitive to different effects.
Additionally we saw that the conformity signal was sensitive to the geometry of the volume. Using SFHs to test for conformity gives us a promising
new way to test for interactions back in time within a volume.
Using spatially resolved SFHs in UVCANDELS
How do regions evolve over time within galaxies? Using the excellent increased resolution of
UVCANDELS we explore internal drivers of galaxy evolutiom with spatially resolved SFHs. After selecting ideal galaxies from the UVCANDELS sample with good detections
in the blue/UV F275W HST filter, we tessellated over the postage stamps to create regions defined by similar signal-to-noise. Given the multiwavelength
SEDs from these regions, we fit the SED in a similar manner as we do with dwarf galaxies and reconstruct the SFH for each region. From this we learn
anout the growth of stellar mass spatially accross galaxies, and we track the evolution of regions around the resolved SFR stellar mass
correlation. We see a negligible change in the slope of the correllation over the past Gyr, but a decrease in the normalizatuon of the relation
as over cosmic time.
Finding the effects of filaments on galaxy SFHs in the New Horizon simulation
Can synchronized star formation in the Local Volume be the result of interaction with a filament?
The NewHorizon simulation has the resolution to analyze low mass galaxies near filaments.
Here we explore how dwarf galaxy star formation histories are affected based on their distance and orientation to filaments, and
explore new ways in which to use galaxy SFHs as a probe of environment.
The role of environment on dwarf galaxy development in LSST
The Legacy Survey of Space and Time from the Vera C. Rubin Observatory will map the southern night sky over the course of 10 years,
creating deep imaging that can trace out cosmic structure from the faintest galaxies. Using knowledge gained from the
New Horizon simulated dwarfs, we will trace interaction with cosmic structure using dwarf galaxy SFHs reconstructed from
Rubin Observations and supplementary VISTA/VIDEO bands in the infrared.
Recognition

Awards:
Robert A. Schommer Prize, The Robert A. Schommer Prize is awarded to the one student
who, in the collective judgment of the astrophysics faculty in the Department, has published
the best first-author, refereed journal article in the field of astrophysics in the past two years
Chambliss Astronomy Achievement Student Awards, AAS 238, The Astronomy Achievement Student
Awards are given to recognize exemplary research by undergraduate and graduate students who present at one
of the poster sessions at the meetings of the AAS,
Rutgers Graduate Student Association Award for Excellence in Graduate Service, Recognizes
a Rutgers University graduate student who demonstrates a tireless track record of service. Those honored
have shown a selfless commitment to the betterment of their cohort, fellow graduate students, and/or the
community as a whole, improving the livelihood of others while encouraging an environment of inclusivity
and growth,
Cal Poly Humboldt Physics and Astronomy Department Award for Outstanding Service to
the Physics & Astronomy Community, Inaugural award given to the graduating student that according
to the department demonstrated exceptional leadership and mentorship..
John Mather Nobel Scholar, The John Mather Nobel Scholarship Program awards travel allowances
towards the cost of presenting research papers at professional conferences. Applicants must have demonstrated
high academic achievement, and be currently holding a Goddard-based research internship
Comap MCM Math Modeling Competition, Honorable Mention, COMAP Mathematical Contest in
Modeling (MCM) challenges teams of students to clarify, analyze, and propose solutions to open-ended
problems. The contest attracts diverse students and faculty advisors from over 900 institutions around the
world.
Media and Public Engagement:
Telescope night at the Clarence Dillon Public Library, Taught families how to use the brand new
telescope the library had acquired
The Astro Show, Video Show by Wyoming Stargazing, Guest speaker, Showcased research for a call in
crowd of amateur astronomers and astronomy enthusiasts alongside regular scientist hosts.
Assigned Scientist at Bachelors (ASAB) Podcast On Space, Special Guest, ASAB is a podcast by
and for trans and nonbinary scientists. As a special guest I talked about my career path, my identity, and
my science..
The Tundra Beyond Space, Video Podcast, Special Guest.
Astrobites Queer Astronomy Pt 1 & 2
Press Release 36 Dwarf Galaxies Had Simultaneous ”Baby Boom” of New Stars, Translated into dozens of
langueages and picked up my Sky & Telescope.
Grants and Fellowships:
LSST DA Catalyst Fellowship The Catalyst Fellowship is a four year
prize postdoctoral fellowship thatworks towards making Rubin LSST science globally
and equitably accessible to fulfill Rubin’s twin promises of breaking scientific barriers
and furthering human knowledge. Within this context, the LSSTC Catalyst Fellowship Program seeks
early-career researchers who aspire not only to conduct their own cutting-edge scientific research,
but also to contribute to the program’s lasting legacy by building networks, learning and sharing skills,
and cultivating practices that enable science with big data.
Noemie Koller Endowed Graduate Scholarship, The Noemie Koller Endowed Scholarship in the
Department of Physics and Astronomy has been established with a gift from Prof. Koller. This
gift was made based on her appreciation of the importance of financial assistance in attracting the
best graduate students. The intent is to assist individual students and the department as a whole.
AAS FAMOUS Travel Grant, The FAMOUS (Funds for Astronomical Meetings: Outreach to Underrepresented Scientists) Travel Grants Program awards money to attend an AAS meeting.
Henry C. Torrey Fellowship, The Torrey award is awarded by the Physics & Astronomy department to
the most outstanding entering graduate students..
Rutgers Excellence Fellowship for doctoral study in Physics and Astronomy, The Rutgers Excellence Fellowship is awarded by the School of Graduate Studies (SGS) to outstanding students entering
doctoral study at Rutgers .


